Learning the Language of Nature
The Science stream of Moran College was established in 1985 with Higher Secondary classes in Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, Biology, English, Alternative English, and MIL, beginning with 25 students and one teacher per subject. The UG General course was introduced in 1987 under Dibrugarh University, followed by the Major course in 2003. The stream came under the deficit system in 1996.
The Physics Department is dedicated to quality teaching, research, and community service. It offers strong academic programs that prepare students for careers in academia, industry, and government.
Vision:
To achieve excellence in teaching, research, and service, and to contribute to scientific advancement at national and international levels.
Mission:
To provide quality physics education, promote research and innovation, engage in community outreach, and foster critical thinking in an inclusive academic environment.
As per the NEP 2020 curriculum of Dibrugarh University, the Department of Physics, Moran College, offers the following programmes with provisions for multiple entry and multiple exit.
|
Programme Name |
Base Programme |
Duration |
Intake Capacity |
|
Under Graduate Certificate Programme in Physics |
FYUGP |
1 Year |
80 (All Together) |
|
Under Graduate Diploma Programme in Physics |
FYUGP |
2 Years |
|
|
Under Graduate Degree Programme in Physics |
FYUGP |
3 Years |
|
|
Under Graduate Honours Degree Programme in Physics |
FYUGP |
4 Years |
|
|
Under Graduate Honours with Research Programme |
FYUGP |
4 Years |
*FYUGP = Four Year Under Graduate Programme
Web Design 101: A Practical approach to create stunning website
LaTeX Essentials: A Hands-on Guide to Professional Typesetting
Excel in MS Excel
Linux Fundamentals: Introduction to Open-Source Computing
Scientific Computing with SCILAB
2022 Saikia, R., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2022, November 20). An analytical solution of Balitsky–Kovchegov equation using homotopy perturbation method. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 37
2021 Lalung, M., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2021). On analytical solutions of proton’s structure functions in the framework of GLR–MQ-ZRS equation. Results in Physics, 28, 104551.
2020 Phukan, P., Lalung, M., & Sarma, J. K. (2020). Small x phenomenology on gluon evolution through the BFKL equation in light of a constraint in multi-Regge kinematics. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 72(2), 025201.
2019 Phukan, P., Lalung, M., & Sarma, J. K. (2019). Studies on gluon evolution and geometrical scaling in kinematic constrained unitarized BFKL equation: application to high-precision HERA DIS data. The European Physical Journal C, 79, 1-25.
2019 Lalung, M., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2019). On phenomenological study of the solution of nonlinear GLR-MQ evolution equation beyond leading order. Nuclear Physics A, 984, 29-43.
2019 Lalung, M., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2019). Small-x analysis on the effect of gluon recombinations inside hadrons in light of the GLR-MQ-ZRS equation. Nuclear Physics A, 992, 121615.
2019 Phukan, P., Lalung, M., & Sarma, J. K. (2019, October). Study of small x behaviour of unintegrated gluon distribution constraining gluon evolution in MD-BFKL equation. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1330, No. 1, p. 012017). IOP Publishing.
2019 Lalung, M., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2019, October). Q2 evolution of gluon distribution function inside the hadrons with both shadowing and antishadowing effects. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1330, No. 1, p. 012016). IOP Publishing.
2017 Phukan, P., Lalung, M., & Sarma, J. K. (2017). NNLO solution of nonlinear GLR–MQ evolution equation to determine gluon distribution function using Regge like ansatz. Nuclear Physics A, 968, 275-286.
2017 Lalung, M., Phukan, P., & Sarma, J. K. (2017). Nonlinear effects in gluon distribution predicted by GLR-MQ evolution equation at next-to-leading order in LHC data. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 56, 3625-3637.
2023 S. Mandal, S. Das, D. J. Gogoi and A. Pramanik, Leading-order corrections to the thermodynamics of Rindler modified Schwarzschild black hole, Physics of the Dark Universe (2023), [arXiv:2308.05712 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi, N. Heidari, J. Kříž, and H. Hassanabadi, Quasinormal Modes and Greybody factors of AdS/dS Black holes surrounded by Quintessence in Rastall gravity, Preprint (2023), [arXiv:2307.09976 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi, J. Bora, M. Koussour, and Y. Sekhmani, Quasinormal Modes and Optical Properties of 4-D black holes in Einstein Power-Yang-Mills Gravity, Annals of Physics 458, 169447 (2023), [arXiv:2306.14273 ]. DOI: 10.1016/j.aop.2023.169447 (Impact Factor 3).
2023 Y. Sekhmani, D. J. Gogoi, M. Baouahi,and I. Dahiri, Thermodynamic geometry of STU black holes, Physica Scripta (2023) (Impact Factor 2.9).
2023 D. J. Gogoi, Ali Övgün and Durmuş Demir, Quasinormal modes and greybody factors of symmergent black hole, Physics of the Dark Universe 42, 101314 (2023), [arXiv:2306.09231 ]. DOI: 10.1016/j.dark.2023.101314 (Impact Factor 5.5).
2023 J. Bora, D. J. Gogoi S. K. Maurya and G. Mustafa, Impact of energy-momentum conservation violation on the configuration of compact stars and their GW echoes, Preprint (2023), [arXiv:2306.01024 ].
2023 N. Parbin, D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Weak gravitational lensing and shadow cast by rotating black holes in axionic Chern-Simons theory, Physics of the Dark Universe 41, 101265 (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.dark.2023.101265 (Impact Factor 5.5) [arXiv:2305.09157 ].
2023 N. Myrzakulov, M. Koussour and D. J. Gogoi, A new f(Q) cosmological model with H(z) quadratic expansion, Physics of the Dark Universe 42, 101268 (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.dark.2023.101268 (Impact Factor 5.5).
2023 Gaetano Lambiase, Reggie C. Pantig, D. J. Gogoi and A. Övgün, Investigating the Connection between Generalized Uncertainty Principle and Asymptotically Safe Gravity in Black Hole Signatures through Shadow and Quasinormal Modes, Eur. Phys. J. C 83, 679 (2023). DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-11848-6 (Impact Factor 4.4). [arXiv:2304.00183 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi, A. Övgün, and M. Koussour, Quasinormal Modes of Black Holes in f(Q) Gravity, Eur. Phys. J. C 83, 700 (2023). DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-11881-5 (Impact Factor 4.4). [arXiv:2303.07424 ].
2023 Y. Sekhmani and D. J. Gogoi, Electromagnetic Quasinormal Modes of Dyonic AdS Black Holes with Quasi-Topological Electromagnetism in a Horndeski Gravity Theory Mimicking EGB Gravity at D → 4, Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys., S0219887823501608 (2023). DOI: 10.1142/S0219887823501608 (Impact Factor 1.873).
2023 M. Koussour, S. Arora, D. J. Gogoi , M. Bennai, P. K. Sahoo, Constant sound speed and its thermodynamical interpretation in f(Q) gravity, Nuclear Physics B 990, 116158 (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.nuclphysb.2023.116158 (Impact Factor 3.045). [arXiv:2303.14138 ].
2023 N. Myrzakulov, M. Koussour and D. J. Gogoi, A New Om(z) Diagnostic of Dark Energy in General Relativity Theory, Eur. Phys. J. C 83, 594 (2023). DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-023-11794-3 (Impact Factor 4.4) [arXiv:2303.04640 ].
2023 R. Karmakar, D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Thermodynamics and Shadows of GUP-corrected Black Holes with Topological Defects in Bumblebee Gravity, Physics of the Dark Universe 41, 101249 (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.dark.2023.101249 (Impact Factor 5.090) [arXiv:2303.00297 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi, Y. Sekhmani et al., Joule-Thomson Expansion and Optical Behaviour of Reissner-Nordström-Anti-de Sitter Black Holes in Rastall Gravity Surrounded by a Quintessence Field, Fortschritte Der Physik 71, 2300010 (2023). DOI: 10.1002/prop.202300010 (Impact Factor 5.532).
2023 N. Parbin, D. J. Gogoi, J. Bora and U. D. Goswami, Deflection angle, quasinormal modes and optical properties of a de Sitter black hole in f(T,B) gravity, Physics of the Dark Universe 42, 101315 (2023) [arXiv:2211.02414 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Tideless Traversable Wormholes surrounded by cloud of strings in f(R) gravity, JCAP 02, 027 (2023). DOI: 10.1088/1475-7516/2023/02/027 (Impact Factor 7.280) [arXiv:2208.07055 ].
2023 R. Karmakar, D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Quasinormal modes and thermodynamic properties of GUP-corrected Schwarzschild black hole surrounded by quintessence, Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 37, 2250180 (2022). DOI: 10.1142/S0217751X22501809 (Impact Factor 1.475) [arXiv:2206.09081 ].
2023 J. Bora, D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Strange stars in f(R) gravity Palatini formalism and gravitational wave echoes from them, JCAP 09, 057 (2022). DOI: 10.1088/1475-7516/2022/09/057 (Impact Factor 7.280) [arXiv:2204.05473 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Quasinormal Modes and Hawking Radiation Sparsity of GUP Corrected Black Holes in Bumblebee Gravity with Topological Defects, JCAP 06, 029 (2022). DOI: 10.1088/1475-7516/2022/06/029 (Impact Factor 7.280) [arXiv:2203.07594 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi, R. Karmakar and U. D. Goswami, Quasinormal Modes of Non-Linearly Charged Black Holes surrounded by a Cloud of Strings in Rastall Gravity, Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 20, 2350007 (2023). DOI: 10.1142/S021988782350007X (Impact Factor 1.873) [arXiv:2111.00854 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Cosmology with a new f(R) gravity model in Palatini formalism, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 31, 2250048 (2022). DOI: 10.1142/S0218271822500481 (Impact Factor 2.547) [arXiv:2108.01409 ].
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Quasinormal Modes of Black Holes with Non-Linear-Electrodynamic sources in Rastall Gravity, Physics of the Dark Universe 33 , 100860 (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.dark.2021.100860 (Impact Factor 5.090) [arXiv:2104.13115].
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, Gravitational Waves in f (R) Gravity Power Law Model, Indian Journal of Physics 96, 637 (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s12648-020-01998-8 (Impact Factor 1.778).
2023 D. J. Gogoi and U. D. Goswami, A new f (R) Gravity Model and properties of Gravitational Waves in it, Eur. Phys. J. C 80, 1101 (2020). DOI: 10.1140/epjc/s10052-020-08684-3 (Impact factor 4.991)





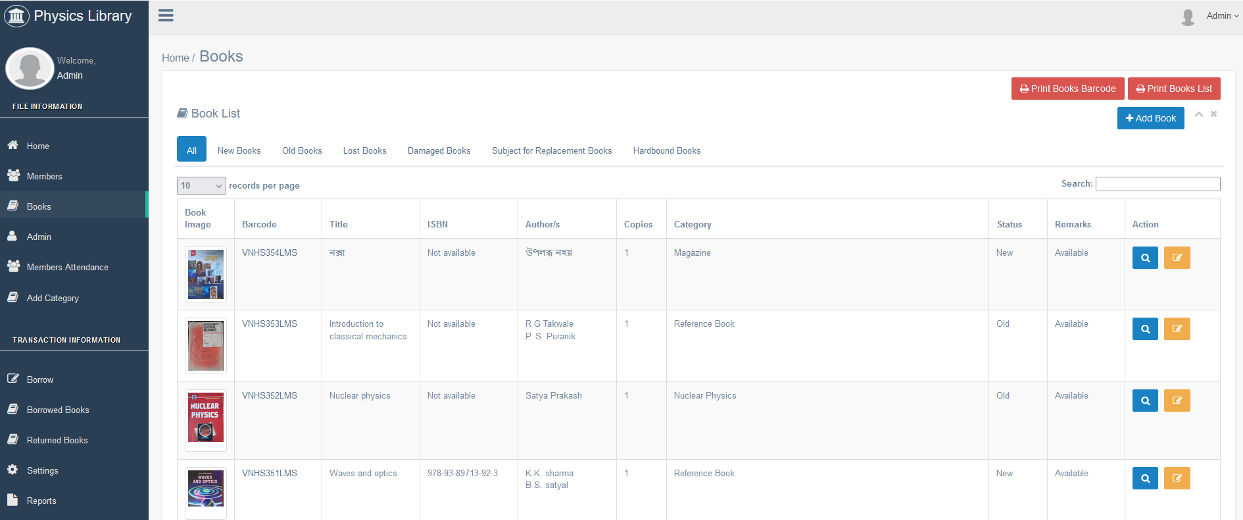
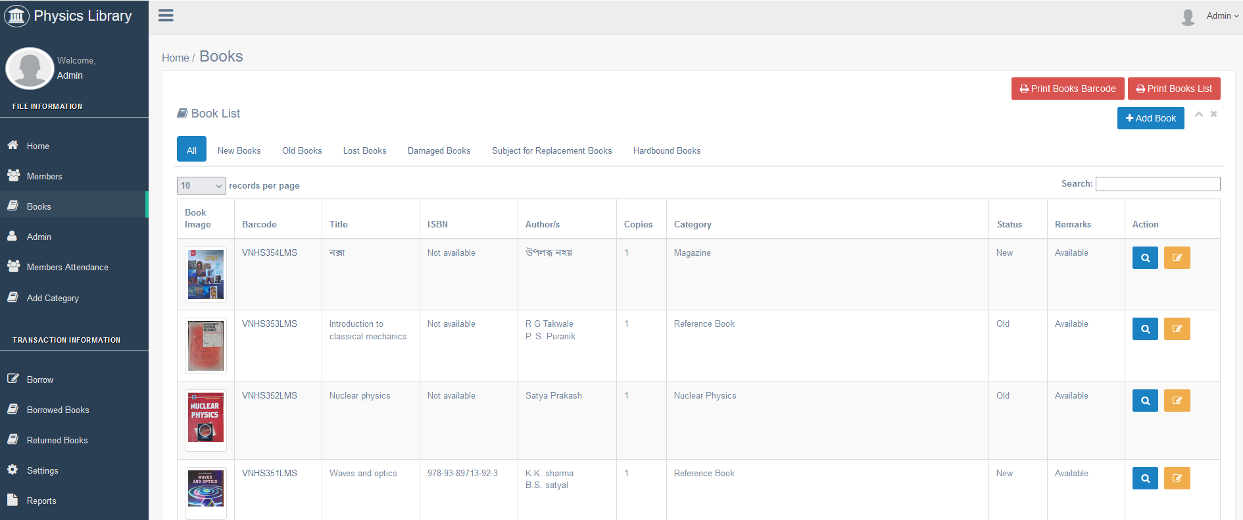
The Department of Physics has developed a comprehensive digital academic ecosystem that integrates library automation, learning management systems, and skill-oriented add-on courses to enhance transparency, accessibility, and student engagement.
A key feature of this initiative is the fully automated Departmental e-Library equipped with an Online Public Access Catalogue (OPAC). Students can access the catalogue digitally, scan QR codes to explore available resources, and manage book issuance, return, and fine records online. This ensures efficient resource management and promotes independent learning habits.
The department also uses the Moodle Learning Management System (LMS) for real-time attendance tracking and academic resource sharing. Attendance is recorded digitally, allowing students to monitor their own attendance status transparently. Course materials, lecture notes, assignments, and announcements are shared through Moodle, creating a centralized and structured learning environment.
To bridge the gap between physics and emerging technological demands, the department offers add-on courses in Information Technology and programming. These courses equip students with computational and analytical skills, enhancing their employability and research capabilities.
This integrated digital approach ensures academic transparency, student empowerment, skill development, and efficient academic administration, making it a distinctive best practice of the Department of Physics.
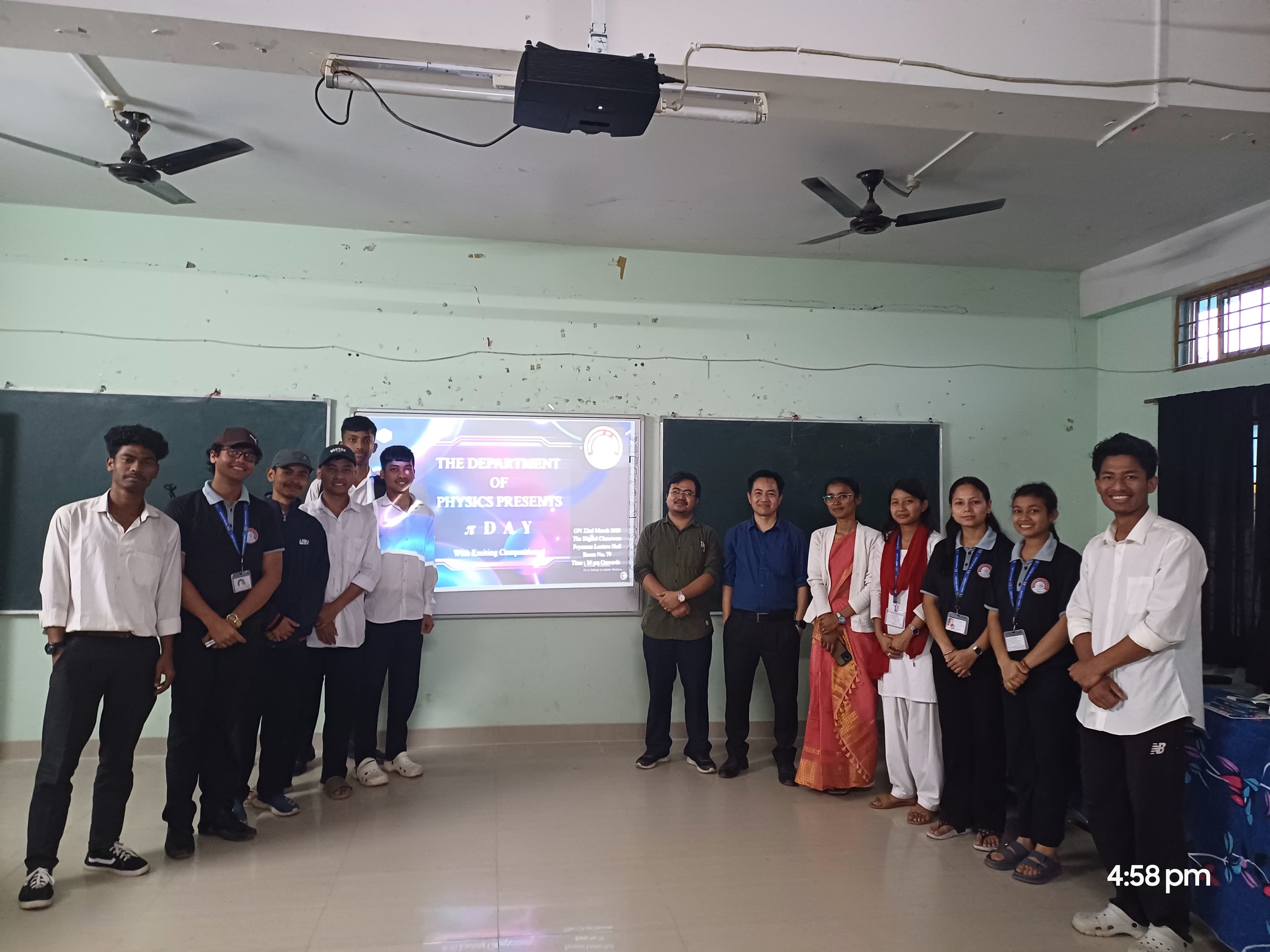


Academic, creative, and cultural highlights of the department
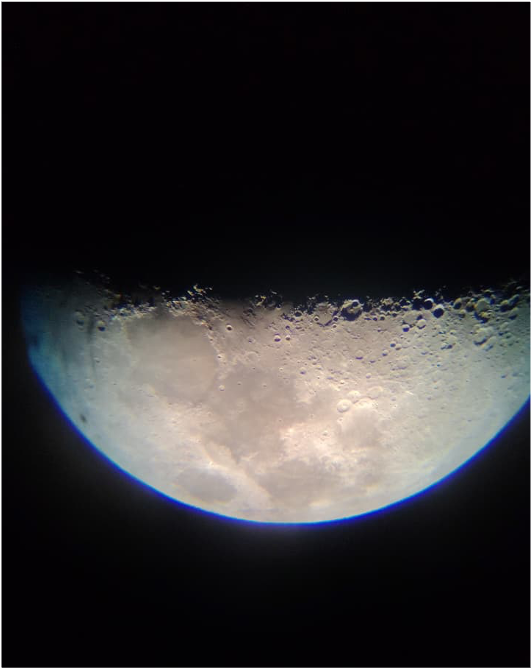

The Department of Physics at Moran College actively engages students and science enthusiasts in astronomy-related outreach and experiential learning activities beyond regular classroom teaching. One of the flagship efforts in this direction is the “Explore the Sky” programme - a sky observation and astronomy workshop designed ...
Read More »